- Unifi Controller Mac Os
- Download Latest Unifi Controller Software
- Unifi Controller Failed To Start Mac
I’m not sure how all these issues occurred at the same time (or at least close enough together to cause issues), but here’s the story:
My Unifi network Controller app is on my 2008 Mac Pro. It has 2 GPUs, the original ATI Radeon HD 2600 XT that supports the Mac boot screen, and a Nvidia 750ti that is a PC card and so doesn’t support the boot screen. The 750ti is my normal gpu, the 2600XT is connected to a smaller monitor that I only use to access the Mac boot screen to switch between Windows 10 and MacOS.
At some point the 2600 XT just stopped working, it doesn’t have any video output from either of the monitor connectors. I’ve pulled it out and reseated it, but it’s just dead. While I was booted in MacOS a couple of days ago I changed the default boot disk to Windows 10 (mistake #1) to access some files from Windows. At that point I started to realize I’d lost a way of getting back into MacOS without a way to get to the boot screen.
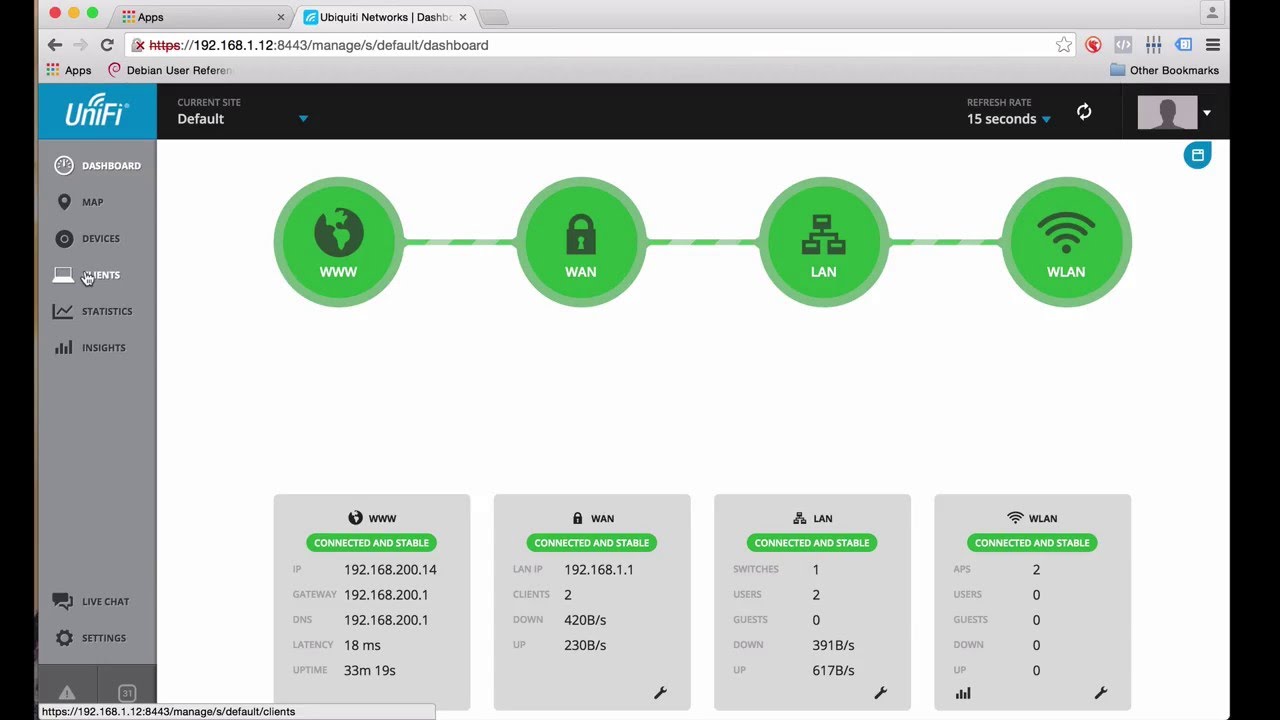
If the new UniFi AP is in the same network as your UniFi controller, your controller should automatically detect the new device with it’s MAC address. The status message notifies you with “ Pending Adoption (UPDATE REQUIRED) “. Simply select Adopt and Upgrade and wait a few minutes until the process is finished. The Unifi controller does not need to be running continuously for basic Unifi access point configuration, you can run it when needed on a Mac, Linux or Windows based desktop although to make use of some of the advanced logging and telemetry functionality it does need to be running constantly and collecting data from associated access points. Jun 23, 2017 Install Unifi Controller on Mac OSX. June 23, 2017 Amber. App name: Unifi Controller; App description: unifi-controller (App: Unifi.pkg). I have downloaded Unifi Controller on my Mac but it either doesn’t open at all or starts to open and browser fails to launch. This seems to be a common problem, lots of detailed advice in posts and I have tried to follow suggestions (eg security / firewall settings) -but I have not yet seen or found an accepted solution. I'm attempting to load Unifi 5.4.16 for the first time, my computer is El Capitan 10.11.6Without any Unifi devices plugged in, it takes too long to load.Server taking too long to start.Start up failed.
Fast forward a few days, I started up my DL380 rack server which I use on a different IP range to the IP range for the rest of the house. I can get to the HP ILO on 10.0.0.2, but I can’t access ESXi which is normally on 10.0.0.3. I can’t get to the Unifi Controller (because it’s on the MacOS disk that I can’t boot) to see what IP that port on the hub has, and running arp -a or using Angry IP scanner is not showing any new IPs getting allocated via DHCP.
My stack of network hubs is under my desk, so getting underneath my desk I realized I’d plugged the DL380 in to the PoE input port and not a network port. While adding another PC to the hub a few weeks back I had moved that port from my 10.x.x.x network back to 192.168.1.x. So now plugging the DL380 network into any other free port on another hub means ESXI still thinks it’s on 10.0.0.3, but I can’t reach it as there’s no route via the port it’s now plugged into.
I need to switch back one of the ports on my Unifi switch back to the 10.x.x.x network, but:
- I can’t boot my Mac Pro to MacOS because it’s stuck in Windows 10
- I need to get a replacement Mac GPU that supports the boot screen
- I can’t switch a port on the Unifi switch back to 10.x.x.x because I can’t access the Unifi controller app
- I don’t have remote access enabled to my Unifi network
- I don’t even know what id/pwd I can use to ssh into the Unifi switch
Next steps:
- Cheap replacement Nvidia GT 120 ordered on ebay for $30.
Last revised 21 November 2017.
- Upgrading
- Tuning Setup
A number of people reached out asking how to configure the Unifi software and access points to work with my pfSense guide so here it is. The Unifi controller does not need to be running continuously for basic Unifi access point configuration, you can run it when needed on a Mac, Linux or Windows based desktop although to make use of some of the advanced logging and telemetry functionality it does need to be running constantly and collecting data from associated access points. I’ve run the Unifi software in a Debian virtual machine on ESXi successfully for a couple of years now. The VM doesnt require a lot of resources, mine is configured as follows:
- Linux Debian 9 64bit
- 1 CPU
- 2GB RAM
- 16GB HD
- single 1gbps VL10_MANAGEMENT network connection
To support full functionality of the Unifi software, make sure that you can access the root account via SSH, the hostname is set and DNS, DHCP and NTP all function.
Connect the unifi access points to your Vl10_MANAGEMENT network, either directly to a PoE switch or making use of one of the included PoE injectors. Make sure to use good quality Cat5e cable, preferably solid core copper if using PoE to ensure adequate current carrying capacity and robust operation. Watch out for stranded and CCA (Copper Clad Aluminum) which are lesser quality.
Install prerequisites
ssh into your Debian VM and log into the root account to perform the following installation steps.
Add Ubiquiti Unifi repository
Pick one of the following repositories:
- deb http://www.ubnt.com/downloads/unifi/debian oldstable ubiquiti
- deb http://www.ubnt.com/downloads/unifi/debian stable ubiquiti
- deb http://www.ubnt.com/downloads/unifi/debian testing ubiquiti
Further details on versions are available on the Unifi community forums. This guide will use the testing branch which at the time of writing this guide covers v5.6.19, the last verison of the 5.6 branch.
echo 'deb http://www.ubnt.com/downloads/unifi/debian testing ubiquiti' | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/100-ubnt.list
Fetch GPG key
apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv C0A52C50
Install Unifi package
This will download and install a number of required packages, verify this completes successfully before proceeding.
start Unifi
Enable unifi to start automatically at boot
and verify the service started correctly by entering systemctl status unifi
Disable default Mongodb instance
Unifi will start its own version of MongoDB so we can and should disable the default instance from running at boot
Open a browser and head to https://
Click +New Wireless Network
- Name/SSID = WIFI-MGMT
- Enabled = [x]
- Security = WPA Personal
- Security key = reallyreallyreallysecurepassword
- Guest policy = [ ]
Open Advanced options and set
- Multicast and broadcast filtering = [ ] (see this section for further details)
- VLAN = [ ] this is untagged native network
- VLAN ID = [ ]
- Enable fast roaming = [ ]
- Hide SSID = [ ]
- WPA Mode = WPA2 Only
- Encryption = AES/CCMP Only
- Group rekey interval = 3600
- User group = Default
- UAPSD = [ ]
- Scheduled = [ ]
- Multicast Enhancement [ ]
802.11 rate and beacon controls = default
Mac filter = default
Radius mac authentication = default
Click Save
VPN network configuration
Click +New Wireless Network
- Name/SSID = WIFI-VPN
- Enabled = [x]
- Security = WPA Personal
- Security key = securepassword
- Guest policy = [ ]
Open Advanced options and set
- Multicast and broadcast filtering = [ ] (see this section for further details)
- VLAN = [x]
- VLAN ID = [20]
- Enable fast roaming = [ ] this is known to cause some issues currently
- Hide SSID = [ ] no additional security
- WPA Mode = WPA2 Only
- Encryption = AES/CCMP Only
- Group rekey interval = 3600
- User group = Default
- UAPSD = [ ]
- Scheduled = [ ]
- Multicast Enhancement [ ]

802.11 rate and beacon controls = default
Mac filter = default
Radius mac authentication = default
Click Save
Clearnet configuration
Click +New Wireless Network
- Name/SSID = WIFI-CLRNET
- Enabled = [x]
- Security = WPA Personal
- Security key = adifferentsecurepassword
- Guest policy = [ ]
Open Advanced options and set
- Multicast and broadcast filtering = [ ] (see this section for further details)
- VLAN = [x]
- VLAN ID = [30]
- Enable fast roaming = [ ]
- Hide SSID = [ ]
- WPA Mode = WPA2 Only
- Encryption = AES/CCMP Only
- Group rekey interval = 3600
- User group = Default
- UAPSD = [ ]
- Scheduled = [ ]
- Multicast Enhancement [ ]
802.11 rate and beacon controls = default
Mac filter = default
Radius mac authentication = default
Click Save
Guest configuration
My guest network is firewalled on the pfSense router and I don’t limit bandwidth for users of the guest network either as I make use of the guest network as a failover network from time to time. Due to these reasons I don’t apply guest policy in the configuration below. Its possible to limit bandwidth and provide access via a portal, I may add these as an addendum to this guide later if theres demand.

Click +New Wireless Network
- Name/SSID = WIFI-GUEST
- Enabled = [x]
- Security = WPA Personal
- Security key = adifferentpassword
- Guest policy = [ ]
Open Advanced options and set
- Multicast and broadcast filtering = [ ] (see this section for further details)
- VLAN = [x]
- VLAN ID = [40]
- Enable fast roaming = [ ]
- Hide SSID = [ ]
- WPA Mode = WPA2 Only
- Encryption = AES/CCMP Only
- Group rekey interval = 3600
- User group = Default
- UAPSD = [ ]
- Scheduled = [ ]
- Multicast Enhancement [ ]
802.11 rate and beacon controls = default
Mac filter = default
Radius mac authentication = default
Click Save
After clicking Save, your wireless networks page should look like this
Configure Services
Configure NTP
In order for access point firmware updates to take place easily from within the web client, we need to an accurate time set. Navigate to Services > NTP and configure the NTP servers. All my devices sync with my pfSense router hence the 192.168.10.1 address.
Controller
Controller settings
Make sure the controller name is set correctly as per your hostname record, in my case of Unifi2
- Controller name = Unifi2 as per your host name
- Controller hostname/IP = unifi2.local.lan FQDN or IP address
Apply changes
Unifi Controller Mac Os
Now we’ve configured all the settings needed to create and configure our SSIDs, we can adopt our access points. Navigate to DEVICES where you should see your access points pending adoption. Adoption is initiated by clicking ADOPT next to the respective access point. After displaying PROVISIONING for a little while, the status should change to CONNECTED.
Once the access point has been adopted you should be able to join any of the provisioned SSIDs. Validate that you can connect, receive an appropriate DHCP address and that you can access internal devices and internet sites.
Click on the access point name and a panel will slide out on the right of the browser window where we can configure access point related settings.
Access point alias
Navigate to General > Alias and set a more meaningful name e.g. Kitchen
Click Save
Download Latest Unifi Controller Software
Band steering
Navigate to General > Band Steering and set Prefer 5G = ON.
This will coerce device promotion from crowded 2.4GHz frequencies into the 5Ghz range.
Airtime fairness
Navigate to General > Airtime fairness and set it to ON.
This will encourage fairer airtime sharing.
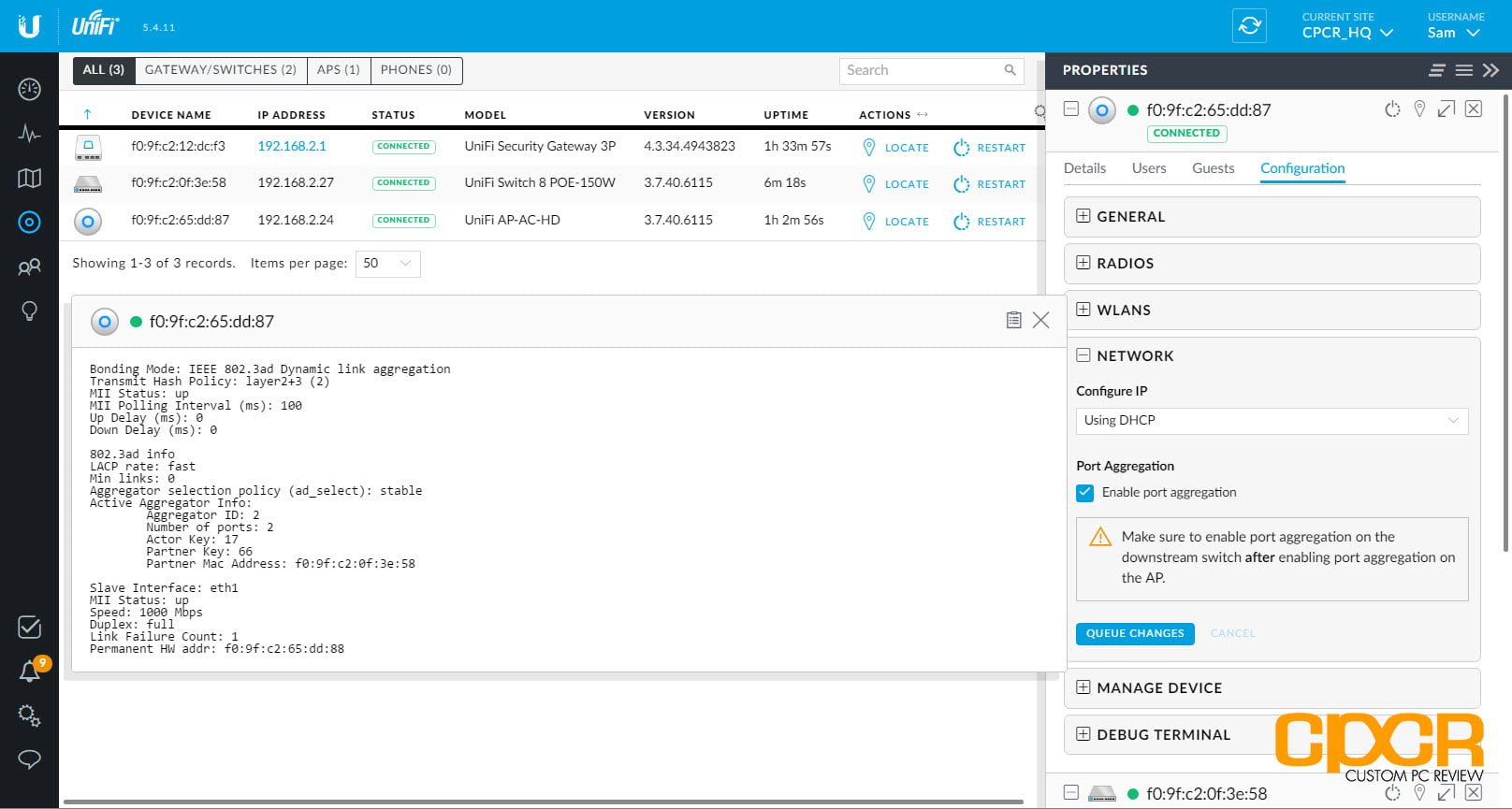
Apply the above changes.
Unifi Software
New software is made available through Unifi and the beta program frequently and its worth keeping up to date. Before updating your system, please make sure to make a backup in case you need to roll back to a previous version. To update your installation SSH into Unifi system and enter wget <filename> -O <destination_filename>, e.g for version 5.7.3 you would enter
wget https://dl.ubnt.com/unifi/5.7.3-91ad2e6240/unifi_sysvinit_all.deb -O ~/unifi/downloads/5.7.3-installer.deb
and to install the .deb package,
sudo dpkg -i ~/unifi/downloads/5.7.3-installer.deb
Once applied its usually worth rebooting. It can take a few minutes for a new install to be accessible due to database conversions so don’t panic if it isn’t accessible immediately.
Access Point firmware
To upgrade an access point with new firmware, click on the access point to be upgraded and navigate to Config > Manage Device > Custom Upgrade. Here is where you enter the link to the firmware and then click Upgrade. In case of issues, its worth noting HTTPS transfers require accurate time to be set. If you are having trouble verify your NTP settings are correct.
Its impossible to produce a guide for tuning access point radios that would work in anything but a small selection of setups, not only are homes and offices wildy different in terms of area and construction, but radio frequency utilisation and pollution will be different too. I want to share a few concepts and ideas that have worked well for me and are likely to work well for a fair percentage of readers.
Access point positioning
Generally keeping the access points with a clear line of sight to the locations where clients are likely to be used, typically this means ceiling mounting. Using a site survey tool like Netspot equips you with actual reading of your access points signal strength across your space. This info can really help establishing the optimal number and placement of access points.
Avoid congested frequency bands
Higher channel widths can support a higher data rates, however the downside is that there are fewer non-overlapping channels available which can lead to congestion problems.
Make use of the inbuilt Unifi RF environment scan which can be accessed under each access points tool menu. Pick non overlapping channels for each access point.
Adrian Grando’s Wifi Explorer is excellent for wifi network inspection. The recently released pro version also enables the use of Metageek’s Wi-spy DBx for frequency analysis.
For 2.4Ghz there are only three non-overlapping channel, 1, 6 & 11, stick to 20Mhz channel widths as increasing to 40Mhz reduces the number of non-overlapping channels and makes using multiple access points difficult. You can see in the above image my 3 access points use 2.4Ghz channels 1, 6 & 11 and 5.4Ghz 36, 52 & 100 to prevent congestion.
For 5Ghz there are many more non-overlapping channels and its possible to configure 40Mhz or even 80Mhz channel widths in certain environments without congestion.
If using the DFS frequency ranges, ensure you aren’t being impacted by nearby RADAR installations or other sources of interference that could cause your access point to reallocate to another channels causing congestion. The Unifi software will alter you in the logging section if this is happening.
Tuning for optimal 5Ghz network usage is more challenging than 2.4Ghz, see this FCC document for a more thorough detailed breakdown of the range.
Radio power
Radio communications depend on clear signals both ways between access point and client. Turning up the transmit power on the access point doesn’t magically solve range problems because although the clients can hear the access point more clearly, they don’t usually have the radio power to be able to transmit back as loudly. You are likely better off turning down the broadcast power and enabling devices to migrate to other more optimal access points where a more balanced communication stream can occur.
Click on each access point in turn and under config, set the transmit powers as follows:
- Radio 2G Transmit power = Low
- Radio 5G Transmit power = Medium
Verify your devices, especilally mobile devices, can still access wifi across your area and verify they transfer to hotspots with better SNR sensibly.
Disable unused 802.11 rates
Depending on the devices in use on your network, you may see some benefits in disabling some of the rates associated with older wifi devices. To disable these frequencies navigate to Settings > Wireless Networks. Edit settings and change the 802.11 rate options as follows:
2G Data rate control
- Enable minimum data rate control = [x]
- Set slider to 12Mbps
- Also require clients to use rates at or above the specified value = [x]
Unifi Controller Failed To Start Mac
5G Data rate control
- Enable minimum data rate control = [x]
- Set slider to 12Mbps
- Also require clients to use rates at or above the specified value = [x]
Save and verify your devices still function correctly.
Block LAN to WLAN Multicast and Broadcast Data
Multicast/Broadcast data is sent at the lowest modulation rate and can negatively affect performance. Unless you absolutely need this feature, it is recommended to block this traffic. If after blocking this traffic you notice difficulty connecting to certain wifi devices, for example printers which may rely on this system for detection, consider adding specfic MAC addresses to the excepted devices before reverting to disabling the block completely. I’ve added an exception for my printer (HP8600), a portable audio speaker (A7) and the subnet gateway (unknown hostname) to support reliable discovery in the image below. See this Ubiquiti document for further information.
21 November 2017
Refined Block LAN to WLAN section
18 November 2017
Added Block LAN to WLAN Multicast and Broadcast Data section
